Removal of weirs
Contents
Introduction
Weirs were considered an important measure to mitigate the impacts from hydropower regulations some decades back. The purpose of these were, at that time, to create larger water-covered areas, primarily for aesthetical reasons. It might also be that they were considered improving the conditions for fish. We would underline that removal of weirs in this context refers to removal of installations within the river used to mitigate impacts from regulations, and not a small dam used as the inlet structure of a hydropower plant. The perceptions on use of weirs as measures to reduce impacts have now changed, as they represent a shift in types of habitats in the favour other species than naturally present, with the consequence that weirs are removed. Weirs can also be a barrier for migration and hence contribute to a fragmentation of the river, and also act as a trap of sediments, as these area as usually slow-flowing areas. The removal of a weir is not a goal in its own unless a careful design of the areas after the removal is made. The area must hence undergo restoration in order to meet the habitat qualities of the fish species of concern. The actual removal of the weir would be to simply use heavy machinery in the river and tear down the physical construction. Removal of weirs is just the first start of the measure, must be followed up by improvement of substrate, river-in-river, etc.
Classification table
|
Fish species measure designed for |
Atlantic salmon (salmo salar) Trout (salmo trutta) |
|
Which life-stage of fish is measure aimed at? |
Spawning / Recruitment Juvenile habitat (0+) Juvenile habitat (1+) Juvenile habitat (older than 1+) Upstream migration |
|
Which physical parameter mitigated? |
Substrate Water velocity Water depth Hyporheic zone |
|
Section in the regulated system measure designed for |
Bypass section Downstream outlet |
|
River type implemented in |
Gravel-bed rivers (weirs are mostly built in sections of the river that have a moderately slope) |
|
Climatic region suitable for |
C: Temperate (mesothermal) climates D: Continental (microthermal) climates E: Polar and alpine (montane) climates |
|
Level of certainty in effect |
Certain |
|
Technology readiness level (maturity) |
TRL8 / TRL9: system complete and qualified / actual system proven in operational environment (competitive manufacturing in the case of key enabling technologies; or in space) |
Methods, tools, and devices
During planning
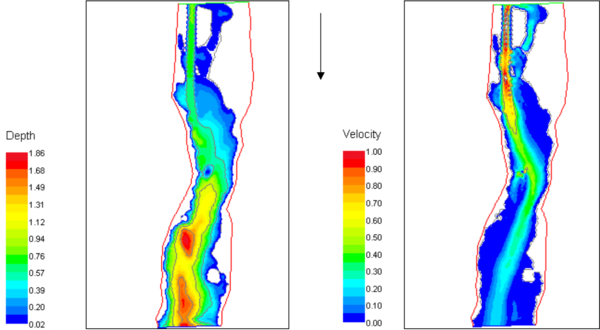
The procedure to assess the impact of weirs on the fish species of concern would be to follow the prescriptions given in the Environmental Design handbook (Forseth & Harby, 2013) where the bottlenecks of the population are identified. In the case that areas with weirs limit the fish population, removal of weirs should be considered. Hydraulic tools are useful in analysing the hydraulic conditions in a river with weirs, and the effect on the hydraulics if the weir is removed. A high number of hydro-dynamic tools are available for such analysis with different functionality and data needs, ranging from more simplistic 1-dimensional (1D) hydraulic tools, to highly advanced 3-dimensional (3D) tools solving a range of partial differential equations (Navier-Stokes) in all directions. The all require details description of the bottom topography of the areas the gravel might be placed, and a flow regime the river will undergo. As average flow velocities (in depth and across the river) will not be sufficiently detailed to identify the best locations, 2D- or 3D models will be required. Examples of such models are River2D, HEC-RAS 2D, Flow2D/3D, Mike21 and OpenFoam.
During implementation
The removal of the weirs would be to simply use heavy machinery in the river and tear down the physical construction. The removal of the weir should be followed up by new measures, which could be to develop a 'river-in-the-river', re-placement of substrate, etc. An evaluation of the hydraulic effect of the removal of the weirs can be done by detailed measuring the area where the weirs have been removed, and then configure and apply a hydraulic model. An evaluation of the biological effect could be done with standard biological methods, such as for instance electro-fishing which will give the densities of juvenile fish.
During operation
Habitat measures in regulated rivers must often be maintained unless the natural functions related to flow and sediments are restored, such as flood events and connectivity of the sediments. The frequency of the maintenance will be very site-specific.